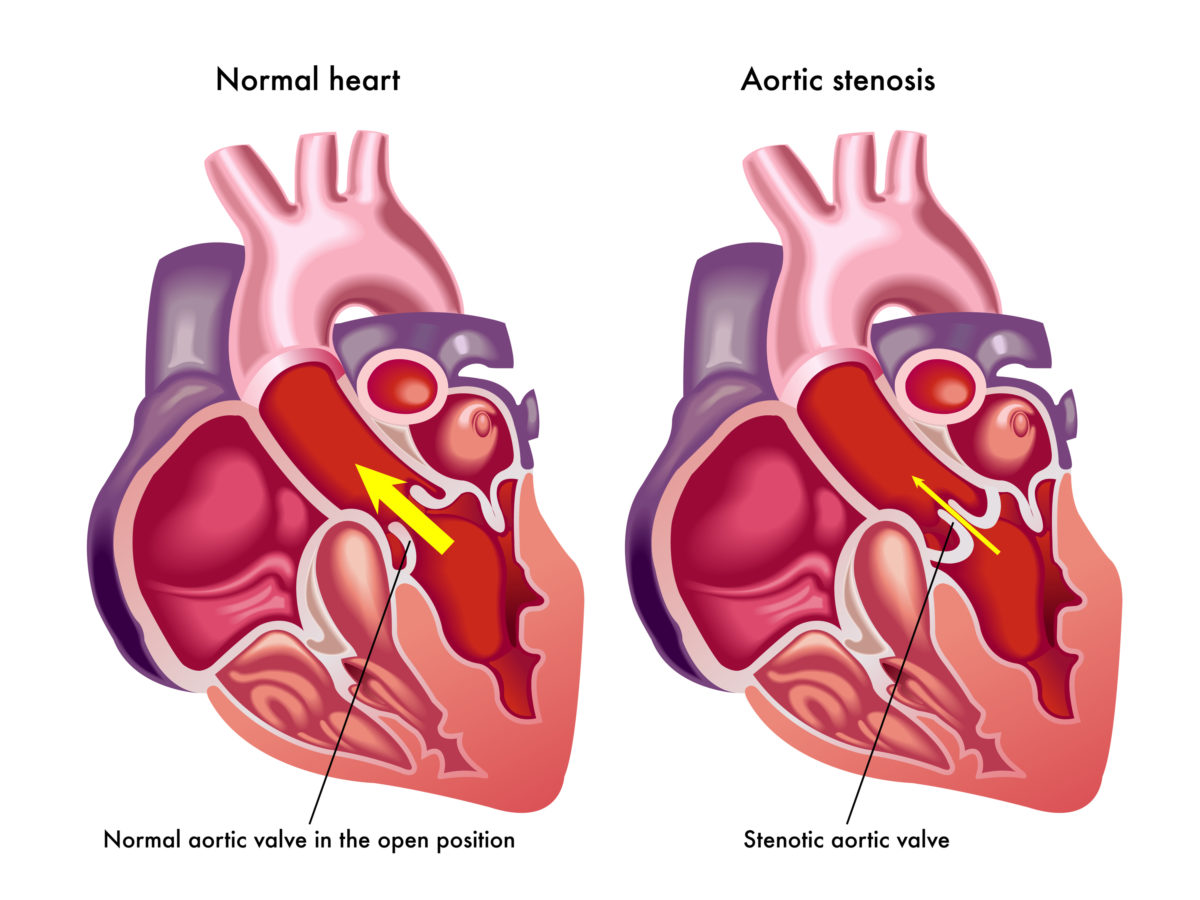
Your doctor just told you that you have a calcified heart valve. One of your heart valves is stenotic. You potentially may need it repaired, or completely replaced. What does this exactly mean? How is there calcium build up on my valve? What is a stenotic valve? Is surgery the only option?
Upon being diagnosed with a type of heart valve disease, a lot of questions are probably buzzing around in your head – as they should be. Remember, never hold back from asking your doctor questions. You have just been diagnosed with mitral valve stenosis, which can be a very serious condition if left untreated. So, you should feel the need to ask and learn everything about this disease.
For this article, we address heart valve calcification/mitral valve stenosis to give you an overview of this disease. First, mitral valve disease is when the mitral valve (located between the left atrium and left ventricle heart chambers) is no longer working properly. When the valve isn’t functioning properly, the heart is unable to pump enough blood out of the left ventricular chamber to give the body oxygen-filled blood. There are different types of mitral valve disease, but for this article, we will focus on mitral valve stenosis (obstruction).
Mitral valve stenosis is when the valve’s opening has narrowed and the valve’s flaps have thickened or stiffened; the flaps may have even fused together, which causes the narrowing or blockage of the valve. When this occurs, blood backs up in the left atrium of the heart instead of flowing to the left ventricle.
When the heart valve becomes calcified, there is a large amount of calcium on the valve, and it has been building up for many years. When the valve becomes calcified, the flaps become stiff and the valve narrows and becomes stenotic. How does this happen? Well, there are a few reasons. Some people’s valves begin to calcify just from age and wear and tear of the valves. Some people are born with congenital valve abnormalities. Some people’s lifestyle choices and history (smoking, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, elevated cholesterol) can lead to calcified valves. Some people’s valves become calcified through atherosclerosis, which is a process that causes arterial blockages in different parts of the body.
A person who has severe stenosis and calcification will experience shortness of breath, chest pain and lightheadedness.
With moderate to severe cases, surgery (valve repair or valve replacement) is usually suggested as the best option to fix the valve and eliminate symptoms. Patients can choose with their doctor whether they want a mechanical or biological heart valve. It’s good to note that even if you get your heart valve repaired or replaced, a biological valve can calcify again.
Unfortunately, there Is no known way to truly prevent the valves from calcifying. However, if a person does have a calcified valve, he or she should be under the watch of a cardiologist, to assess if the valve worsens over time. The cardiologist will most likely want to follow up in 6 months to a year. Treatment, such as surgery, will be suggested when deemed necessary.
Are you suffering from valve stenosis or calcification and looking for a surgeon? Dr. Peter Mikhail is a cardiac surgeon who specializes in performing surgeries on mitral and aortic valves. Dr. Mikhail is based in New Port Richey, FL, and treats patients in the Tampa and Clearwater areas. To book a consult, click here or call 727-312-4844.